Imagine sitting across from a loan officer, heart racing, only to hear those devastating words: “Your loan application has been denied.” For millions of Americans, this scenario is a harsh reality, often boiling down to one critical factor: credit score.
The impact of credit score on loans is both profound and far-reaching, capable of transforming your financial journey from constant rejection to assured approval.
This guide is your roadmap to understanding how credit scores shape loan opportunities, decode the mysterious world of credit, and provide you with actionable strategies to take control of your financial destiny.
Whether you’re a first-time borrower or someone looking to improve your financial standing, you’ll discover how your credit score is the key that can unlock—or lock—your financial potential.
Table of Contents
What Exactly is a Credit Score? Breaking Down the Basics
Your credit score is more than just a number—it’s a financial fingerprint that tells lenders a story about your financial reliability.
This three-digit score, typically ranging from 300 to 850, is a mathematical representation of your creditworthiness, calculated based on your financial history and behavior.
Key Components of a Credit Score:
- Payment History (35%): Your track record of paying bills on time
- Credit Utilization (30%): The amount of credit you’re using compared to your total available credit
- Length of Credit History (15%): How long you’ve been managing credit
- Credit Mix (10%): The variety of credit types you’ve handled
- New Credit Inquiries (10%): Recent applications for new credit
Credit Score Ranges:
| Credit Score Range | Rating | Loan Approval Likelihood |
| 300-579 | Poor | Very Low |
| 580-669 | Fair | Limited |
| 670-739 | Good | Moderate |
| 740-799 | Very Good | High |
| 800-850 | Exceptional | Very High |
The two most common scoring models are FICO and VantageScore, with FICO being the most widely used by lenders. Understanding these scores is crucial to comprehending the true impact of credit score on loans.
The Direct Impact of Credit Score on Loan Approval
When it comes to loans, your credit score is essentially a risk assessment tool for lenders. It’s their crystal ball into your financial reliability, helping them predict the likelihood of you repaying borrowed money.
How Credit Scores Influence Loan Approvals:
- Mortgage Loans: Most lenders require a minimum credit score of 620
- Personal Loans: Typically require scores between 600-700
- Auto Loans: Scores above 660 often secure the best rates
- Business Loans: Higher scores can mean easier approval and better terms
- Credit Card Applications: Scores below 670 often result in higher interest rates or denial
Statistically, borrowers with lower credit scores are significantly more likely to default on loans. This is why lenders use credit scores as a primary screening mechanism, making the impact of credit score on loans absolutely critical.
Beyond Approval – How Credit Scores Affect Loan Terms
Loan approval is just the beginning. Your credit score dramatically influences the actual terms of your loan, potentially saving or costing you thousands of dollars.
Loan Term Variations Based on Credit Scores: | Credit Score | Avg. Interest Rate | Max Loan Amount | Down Payment | |————-|——————–|—————–|————–│ | 580-669 | 6.5% | $250,000 | 10% | | 670-739 | 5.0% | $350,000 | 5% | | 740-799 | 3.5% | $500,000 | 3% |
For example, on a $300,000 30-year mortgage:
- A borrower with a 620 credit score might pay around $1,841 monthly
- A borrower with a 740 credit score could pay approximately $1,491 monthly
- Total difference over 30 years: Over $125,000!
Common Loan Rejection Reasons Related to Credit Scores
Understanding why loans get rejected can help you address potential issues proactively.
Top Loan Rejection Reasons:
- Credit scores below lender’s minimum threshold
- High credit utilization (over 30% of available credit)
- Recent late payments or missed bills
- Short or inconsistent credit history
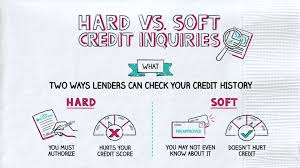
- Too many hard credit inquiries in a short period
- Recent bankruptcies or collections
Strategies to Improve Your Credit Score for Better Loan Opportunities
Improving your credit score is a strategic process that requires patience and discipline.
Proven Credit Score Improvement Strategies:
- Pay all bills on time, every time
- Reduce credit card balances to below 30% of credit limits
- Avoid opening multiple new credit accounts simultaneously
- Keep old credit accounts open to maintain credit history length
- Regularly check credit reports for errors
- Consider a secured credit card if building credit from scratch
Pro Tip: Set up automatic payments and use credit monitoring services to stay on top of your credit health.
The Hidden Costs of a Poor Credit Score
A low credit score doesn’t just affect loan approvals—it has far-reaching financial consequences.
Long-Term Financial Impacts:
- Higher lifetime interest payments
- Limited financial opportunities
- Increased insurance premiums
- Potential employment challenges
- Restricted housing and rental options
Imagine losing over $100,000 in potential savings just because of a low credit score. This demonstrates the profound impact of credit score on loans and overall financial well-being.
Credit Score Myths vs. Reality
Debunking Common Credit Score Misconceptions:
- Myth: Checking your credit score hurts your credit Reality: Soft inquiries don’t impact your score
- Myth: You only have one credit score Reality: Multiple scoring models exist
- Myth: Closing credit cards improves your score Reality: This can actually lower your credit score
Conclusion
Your credit score is more than a number—it’s a powerful financial tool that can open or close doors to opportunities. By understanding the impact of credit score on loans, you’re already taking the first step toward financial empowerment.
Remember, improving your credit is a journey, not a destination. Small, consistent steps can lead to significant financial transformations.
Skale Money Key Takeaways
- Credit scores directly influence loan approvals and terms
- Scores range from 300-850, with higher scores offering better opportunities
- Proactive credit management can save tens of thousands of dollars
- Regular monitoring and strategic improvements are key
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. How often should I check my credit score?
At least once a year, or before major loan applications. Many credit card companies now offer free monthly credit score updates.
2. Does checking my credit score hurt my credit?
No, soft inquiries (like checking your own score) do not impact your credit.
3. How long does it take to improve a credit score?
Significant improvements can be seen in 3-6 months of consistent, positive financial behavior.
4. Can I get a loan with a bad credit score?
Yes, but with higher interest rates and less favorable terms. Some lenders specialize in bad credit loans.
5. What’s the fastest way to improve my credit score?
Pay bills on time, reduce credit card balances, and avoid opening multiple new credit accounts simultaneously.
![]()