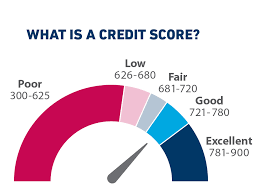
In the complex landscape of personal and business finance, credit scores are much more than simple numbers. They are powerful indicators that can make or break financial opportunities across every stage of your professional journey.
From a budding entrepreneur launching a startup to a corporate executive managing complex financial portfolios, understanding the nuanced types of credit scores is crucial for financial success.
Skale Money Key Takeaways
- Understand the primary types of credit scores used in financial decision-making
- Learn how different credit scoring models impact personal and business finances
- Discover strategies to improve and maintain healthy credit across different scoring systems
- Recognize the importance of credit scores in various financial milestones
Table of Contents
The Basics of Credit Scores
Credit scores are the financial world’s report cards, providing a snapshot of an individual’s or business’s creditworthiness.
These numerical representations have become critical tools in evaluating financial reliability, offering lenders, investors, and financial institutions a quick way to assess risk.
Key Points of Credit Scores
- A credit score is a three-digit number ranging typically from 300 to 850
- Scores are calculated based on credit history, payment behavior, and financial habits
- Different types of credit scores exist for various financial purposes
- Credit scores impact loan approvals, interest rates, and financial opportunities
FICO Score – The Industry Standard
When discussing types of credit scores, the FICO score undoubtedly takes center stage. Developed by the Fair Isaac Corporation, this scoring model has been the gold standard in credit assessment for decades.
Most lenders rely on FICO scores when making critical financial decisions.
Understanding FICO Score Components
- Payment History (35%): Tracks your record of paying bills on time
- Credit Utilization (30%): Measures how much of your available credit you’re using
- Length of Credit History (15%): Considers the age of your oldest and newest accounts
- Credit Mix (10%): Evaluates the diversity of your credit accounts
- New Credit (10%): Examines recent credit inquiries and new account openings
| FICO Score Range | Credit Rating | Potential Impact |
| 800-850 | Exceptional | Best loan terms, lowest interest rates |
| 740-799 | Very Good | Favorable rates, high approval chances |
| 670-739 | Good | Standard rates, moderate approval odds |
| 580-669 | Fair | Higher interest rates, limited options |
| 300-579 | Poor | Significant challenges in obtaining credit |
VantageScore – The Modern Alternative
As one of the alternative types of credit scores, VantageScore emerged as a collaborative effort by the three major credit bureaus.
It offers a more inclusive approach to credit scoring, particularly beneficial for individuals with limited credit history
.
VantageScore Key Characteristics
- More inclusive scoring methodology
- Faster updates to credit profiles
- Considers alternative financial data
- Helpful for those with limited credit history
Key differences from FICO include:
- More lenient scoring for new credit users
- Considers rental and utility payments
- Faster response to positive credit changes
Industry-Specific Credit Scores
Not all types of credit scores are created equal. Different industries develop specialized scoring models tailored to their unique risk assessment needs.
Specialized Credit Score Types
- Auto Lending Scores: Focused on predicting auto loan repayment
- Credit Card Industry Scores: Tailored to credit card approval risks
- Mortgage-Specific Scores: Detailed assessments for home loan potential
- Insurance Credit Scores: Evaluate risk for insurance policies
- Business Credit Scores: Assess company financial health
Credit Scores for Entrepreneurs and Startups
For entrepreneurs, credit scores transcend personal financial metrics—they’re critical tools for securing business funding and establishing credibility.
Critical Considerations for Startup Founders
- Personal credit directly influences initial business opportunities
- Separate personal and business credit profiles
- Build business credit systematically
- Maintain low credit utilization
- Diversify credit sources
Pro Tip: Young entrepreneurs should focus on building a strong personal credit score before seeking business financing. Many early-stage funding decisions rely heavily on the founder’s personal credit history.
Corporate Credit Scoring
As businesses grow, credit assessment becomes more sophisticated. Corporate credit scoring involves complex evaluation methods that extend beyond individual credit metrics.
Corporate Credit Assessment Factors
- Annual revenue and financial statements
- Payment history with suppliers and vendors
- Length of business operational history
- Industry-specific financial performance indicators
- Debt-to-income ratio for businesses
Improving and Maintaining Healthy Credit Scores
Maintaining excellent credit requires strategic financial management and consistent monitoring across different scoring models.
Practical Strategies for Credit Improvement
- Pay all bills consistently and on time
- Keep credit utilization below 30%
- Maintain a diverse credit mix
- Regularly monitor credit reports
- Avoid unnecessary credit inquiries
- Address errors promptly
| Action | Impact on Credit Score | Time to See Results |
| Timely Bill Payments | Significant Positive | 1-3 months |
| Reduce Credit Utilization | Moderate Positive | 1-2 months |
| Minimize New Credit Inquiries | Prevents Negative Impact | Immediate |
| Correct Credit Report Errors | Potential Major Improvement | 30-45 days |
Future of Credit Scoring
The landscape of types of credit scores continues to evolve, with emerging technologies reshaping financial assessment methodologies.
Emerging Trends
- Artificial intelligence in credit scoring
- Integration of alternative data sources
- Real-time credit profile updates
- Increased personalization of risk assessment
- Greater emphasis on financial behavior patterns
Conclusion
Credit scores are dynamic financial tools that evolve alongside your professional journey. Understanding the various types of credit scores empowers you to make informed financial decisions, unlock opportunities, and build a robust financial foundation.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How often do credit scores change?
Credit scores can update monthly, depending on reported financial activities and changes in your credit profile.
Can I have different credit scores from different agencies?
Yes, different agencies may use slightly different scoring models, resulting in minor variations in your credit scores.
How long do negative items affect my credit score?
Most negative items remain on credit reports for 7-10 years, gradually losing impact over time.
Do business and personal credit scores impact each other?
For small businesses and entrepreneurs, personal credit often directly influences business credit opportunities.
Are there free ways to check my credit score?
Many credit card companies, financial websites, and credit bureaus offer free credit score monitoring services.
Disclaimer: Always consult with a financial advisor for personalized credit and financial guidance.
![]()